
Last month we talked about offsite engagement for awareness, appearing at the right point in a consumer’s thought process, introducing a brand as a topic expert and potential option.
The next step along the route to revenue looks at the “Consideration” phase where engagement – as well as other factors – can affect click-through rates (CTR) in search results, an oft overlooked, and underrated metric in the world of SEO.
First a caveat! CTR studies are both fun and farcical. When no two search results are the same, predicting the percentage of click-throughs in certain positions, and leveraging that as a prognostication of actual traffic can, at best, provide directional data and, at worst, leave clients unhappy when targets fall short.
What Can SEO Affect in the SERP?
- When: This component refers to the searches that return your site (or your client’s site) as a relevant result. Through query research SEO practitioners can affect when their site appears in the SERP. In an earlier article I covered an intent-based approach that leverages consumer behavior data throughout the decision journey to help marketers drive content development and search query relevance.
- Where: This component refers to your websites’ placement and rank within the SERP. The wherecomponent relies on core optimization, the site’s ability to be properly indexed and cataloged, and whether its content is relevant to the user query. If you’re a savvy SEO you understand the core concepts of the art and science; Platform/architecture, content relevance, offsite authority building, onsite engagement and social signals. (Rinse and repeat!)
- What: This component refers to the type of result that appears for a specific query. For instance, does the search engine present universal, local, news or other non-traditional results? Obviously, sites will only rank and appear for media specific queries if they have produced, optimized and distributed that specific type of content on their site and / or across various channels. Examples include; social platform profiles, YouTube videos, Google+ Local profiles, LinkedIn, owned images and / or news. SEO’s can influence both the existence and optimization of these kinds of assets.
- How: This component is the key to of SERP engagement. Below we’ll dig a little deeper into how the results look, their familiarity, clickability and overall relevance to the search query.
The how can manifest in a number of different ways, i.e.:
- Markup
- Authorship
- Title
- Snippet
- Bolding
- Link
- Breadcrumbs
|
- Sitelinks
- Images
- Videos
- News
- Social signals
- Local
- Mobile
|
Although (unfortunately for SEO) SERP display is dependent on search engine whim, we can affect – at least in today’s SERP – some of these elements and positively impact click through rates.
Take a look at the following example for the query [perfect santa monica beach hotel]:
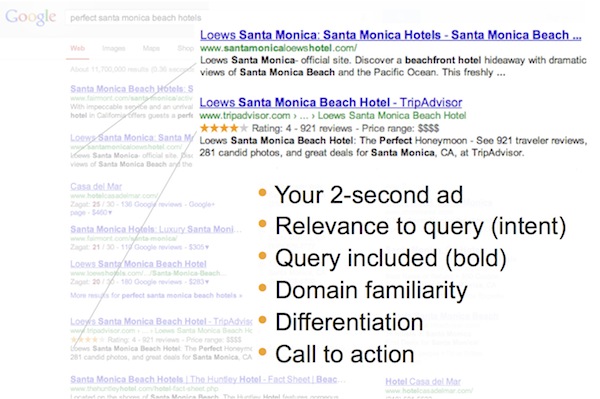
Let’s intelligently assume the user has decided on location (Santa Monica), near the beach, and used the modifier “perfect”, which means they’re looking for some qualifier that this isn’t a horrible hotel.
Google maps the query to Loews Santa Monica Beach Hotel (the official name). Loews’ site appears in the second organic position and in a three-pack of local results. Not too bad!
Recent studies have shown users spend an average 14.7 seconds looking at the organic search results – with 8-15 results on a results page, that’s about 2 seconds per listing to grab attention.
How Can Your Result Stand Out?
Way back in sixth position is TripAdvisor, a travel review site that does a great job in doing exactly that; addressing the user’s intent, capturing attention, and inspiring the click.
Here are a few strategies to call out your result in the SERP:
Rich Snippets markup provide the ratings, reviews count, and price range. Listing the full name of the hotel as the first part of the title tag and meta snippet creates a bold repetition of the original query, adding in some dynamic insertion into the snippet also grabs a users attention – “See 281 candid photos”! Note: Using the word “see” as the call to action, underscores a human curiosity to take a peek at something… candid? (A little naughty perhaps… I must see those!).
Add in the brand recognition of TripAdvisor, and I’d be almost certain the click through rates for this query would be skewed towards the listing in position #6 over standard CTR analysis (This is a great CTR analysis of different types of query from SEOMoz).
Richer Results. For queries that Google believes warrant richer results, the “Search Everywhere Optimization” approach outlined in last month’s article holds true. Rich media can almost always result in better engagement and garner more user clicks than static text links. Users posing questions as search queries generally have Google mapping to “how to” videos or images.
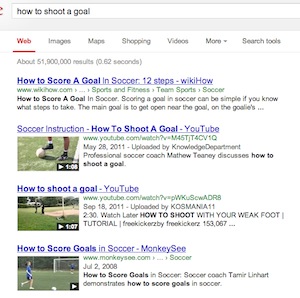
Note: This kind of search intent can be capture through the creation of specific question based content. (see examples below)
 |
 |
|
Video!
|
Images! Authorship!
|
Notice how different questions – action vs. activity – can garner different media results.
Google knows that questions around action-based topics are probably better satisfied by video, whereas activity-based topics, are probably better served by images and articles.
Google doesn’t inherently know this, but leverages it’s massive data set of user behavior (such as clicks/dwell rates), human reviewers and semantic interpretation of content to connect search intent to relevant content/media types.
The example on the right, also includes an Authorship SERP element, a necessity for experts and expert wannabes to ensure articles pull image and author information into the results – a very engaging element!
How to Get People to Engage (Click)
- Build a brand! Last time we talked about building off-site awareness. Leveraging offsite promotions, creating associations and affiliations can inspire users to click through when they see your name (and Google loves brands!)
- Pay attention to the title tag and meta description of your page. Do they tell enough of a story about what users will get from a click, and is it differentiated from your competition (if you aren’t doing research in the SERP by actually searching on your “money queries,” then you don’t deserve the click!)
- Core optimization is key. Not just around on page and in code tag optimization. Look at your site structure, internal linking and how people are navigating your site to help create breadcrumbs in your search results (look at the TripAdvisor example above).
- Are you using rich snippets? Google will like you more if you do… they even give you the tools to make it easier to see how well you’re doing! Markup your data!
- Authorship is a buzzword, but an important one! Google tells you how, and I suggest you run – don’t walk – to implement… and then write some great content!
- Think multimedia! Especially around explanations of products, services or expertise. Create video and image assets, tag them, caption them, *optimize* them and promote them!
- Review the SERP! Having a great looking result is one thing, having the best looking result can bring you more and better traffic. Review often. Tweak. Test. Engage!
Although this article can only scratch the surface of SERP engagement, ask yourself the when, where, what and how.
Starting with: How will I improve SERP engagement with click-worthy results?



