Something that always plays on an SEO mind, either in-house or agency, is this: what is the competition doing? Reverse-engineering competitors’ organic SEO strategies can lead to a lot of actionable findings that help improve your – or your client’s – strategy.
Being able to distinguish and put your finger on what your competitors are doing, especially when they’re outperforming you, is a huge plus. This list of individual methods will allow you to do that, and rein your competition in as a direct result.
Site Structure
Having your website’s information architecture and overall site structure is a key part in performing well in organic search. This is split into different aspects:
- Following best practice from a technical standpoint
- Providing a good user experience to increase the chance of customer retention
- Internal link structure
- Page depth
1. Information Architecture
A fundamental area to look at is how your competitors’ websites are structured in comparison to yours. This will give you a really good understanding of how they’re set up, not only for organic search, but also for customer journeys.
To get a thorough understanding of how your competitors’ websites are structured, run a ScreamingFrog crawl on the website and enable the “Tree” view. This view shows you how the IA is designed and gives you an indication of how they pass link juice down from the main domain to the rest of the website.

When comparing the IA of competitors against you, the key things to look at are:
- How deep are the pages/URLs that rank for your main keywords compared to yours?
- Is the IA much smaller? If so, spread of link juice is higher.
- How the URL structure works with the IA – for example, do they keep URLs closer to the domain than your website?
2. Spread of Page Depth
Another key area on ScreamingFrog to analyze against your competitors is the Site Structure tab, as this shows you the proportion of pages that are at each level of depth within the website – see image below.
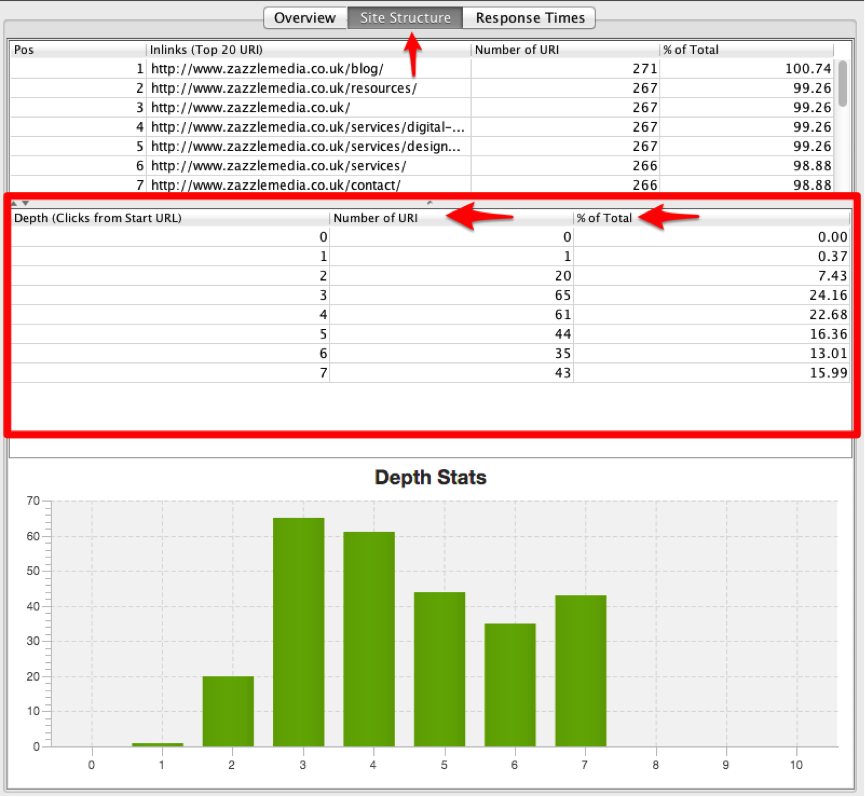
When comparing your website to your competitors with this part of the tool, look at the difference in number of pages at each level. This gives you an overall trend of how the IAs differ.
The graph produced by ScreamingFrog is a great visual representation of this, but the numbers to take into account are the “Number of URI” at each Depth – compare these to your competitors and it gives you an overall sense of how the two websites differ.
For example, if you have more URIs at the depth of seven than your competitor, you know that your content may be surfaced too deep for both the user and Google to find.
3. Internal Link Structure
There are a vast number of ways to see an overview of your own internal link structure and the best method is downloading Google Webmaster Tools’ internal links report – see image below.
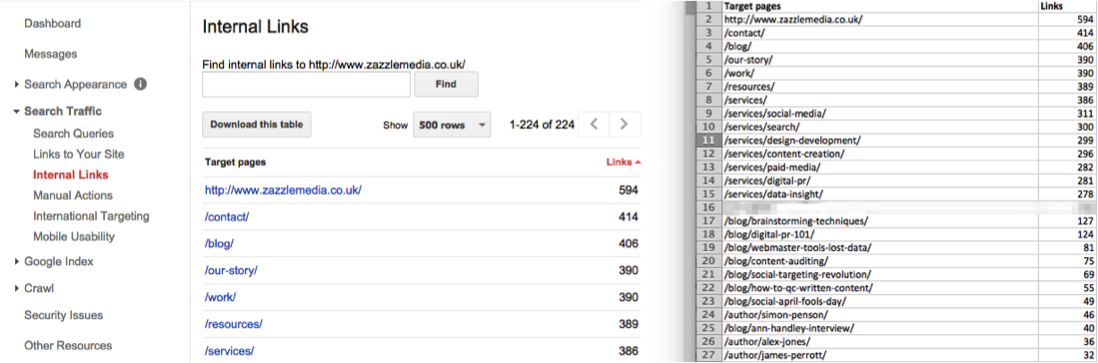
However, you do not have access to your competitors’ Webmaster Tools account. The best way to see this is to run a ScreamingFrog crawl of your competitor and conduct a bulk export of all inlinks – this is an option in the menu.
This exports all manual links from the website. With simple filters applied, you are able to replicate what Webmaster Tools produces for your own website. A direct comparison is then made available and you can see into the internal linking strategy that your competitor is executing.
4. Page-Level Analysis: UX
It’s important to understand page-level user experience, especially in regards to readability – Dale-Chall, Flesch Kincaid Grade Level, Flesch Kincaid Reading Ease Score, Gunning Fog, and Smog Index. This will give you a direct comparison of how easy your content is to digest against direct competitors.
Another factor to take into account is page speed for both desktop and mobile. Since the launch of Google’s mobile algorithm update, page speed, particularly at mobile level, has become a new priority.
Matt Cutts loosely announced that page speed is a minute ranking signal, and we believe it is, as it’s a very important user experience factor.
“‘White hat’ search engine optimizers often improve the usability of a site, help create great content, or make sites faster, which is good for both users and search engines.” – Matt Cutts.
URL profiler looks at all of the following metrics that cover off technical, on-page content, content quality, keywords assigned to pages:
Technical:
- URL
- Content Length
- HTML Length
- Text Length
- Text-to-HTML Ratio
On-page content:
- Word Count
- Paragraph Count
- Reading Time
- Word 1 on page
- Word 2 on page
- Word 3 on page
- Word 4 on page
- Word 5 on page
Content score:
- Sentiment
- Sentiment Score
- Dale-Chall Score
- Flesch Kincaid Grade Level
- Flesch Kincaid Reading Ease Score
- Flesch Kincaid Reading Ease
- Gunning Fog Score
- Smog Index
Mobile-friendly:
- Mobile Friendly
- Mobile Friendly Score
- Uses Incompatible Plugins
- Content Wider Than Screen
- Links Too Close Together
- Text Too Small to Read
- Mobile Viewport Not Set
- Robots.txt Blocked Resources
- Resources Failed
- Mobile Friendly URL
- Page Speed Device
- Mobile Speed Score
- Usability Score
- Avoid Plugins
- Size Content to Viewport
- Size Tap Targets Appropriately
- Use Legible Font Sizes
- Configure Viewport
- Optimize Images
- Prioritize Visible Content
All of these metrics provided by URL profiler allow you to understand how code heavy your competitor’s website is, on-page keyword relevance, content/readability score, and mobile friendliness.
5. Site:domain.com
The overall size of a site gives you an indication of a number of different things; the amount of pages/products they have listed, the amount of content on the website and the general “size and feel” of the business.
If you Google site:competitorwebsite.com, this produces search results for only those that Google has crawled of that specific website. Note down the number of total pages indexed by Google and compare it to your website. This is the quickest way to see how Google has indexed the website and how many pages.
Disable JavaScript and reload site – UX
To see the makeup of each competitor website and how Google views it, there are two key ways that you can see this.
First, after you have run a site:competitorwebsite.com search, view the cached result – shown below.
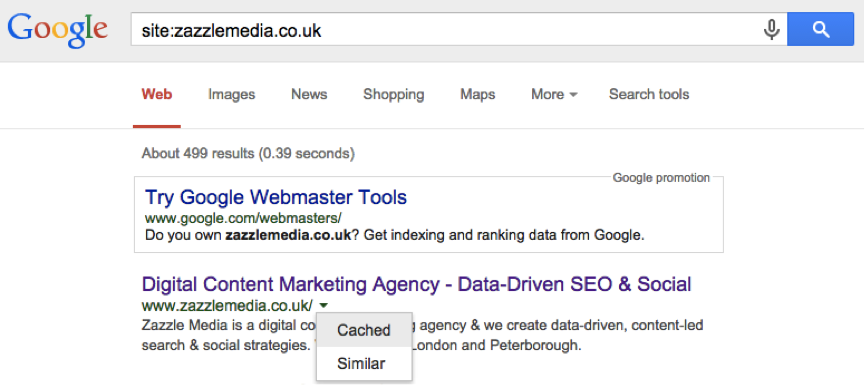
This shows you how Google views the website with its crawler, then to gain further insight, select the “Text-only” version to see how Google orders the content.
The second way to see how Google and other search engines view the website is to disable JavaScript on your browser and reload the website. This shows you how JavaScript reliant the website is. Google is getting better at understanding JavaScript, especially with the release of their own JavaScript base Angular.js – but having Java heavy websites is still not recommended.
6. Mobile and Organic Search Visibility
One of the best ways to get a general gauge on organic performance of any competitor is to analyze their search visibility. This can be done through a few different tools: SearchMetrics, SEMrush, SISTRIX, and more.
Search visibility is measured by the keywords that a website ranks for, the volume for those keywords, and the click-through rate assigned to the position that they rank for – this creates their own indexes/weighting.
SearchMetrics has recently introduced mobile visibility, which is really useful as this highlights any discrepancies between desktop and mobile organic visibility. For example, if desktop organic visibility was significantly higher than mobile, that suggests that the website is not mobile-friendly.
Another useful part of SearchMetrics is the comparison tool, which shows you how one website’s organic visibility compares to another – see below.
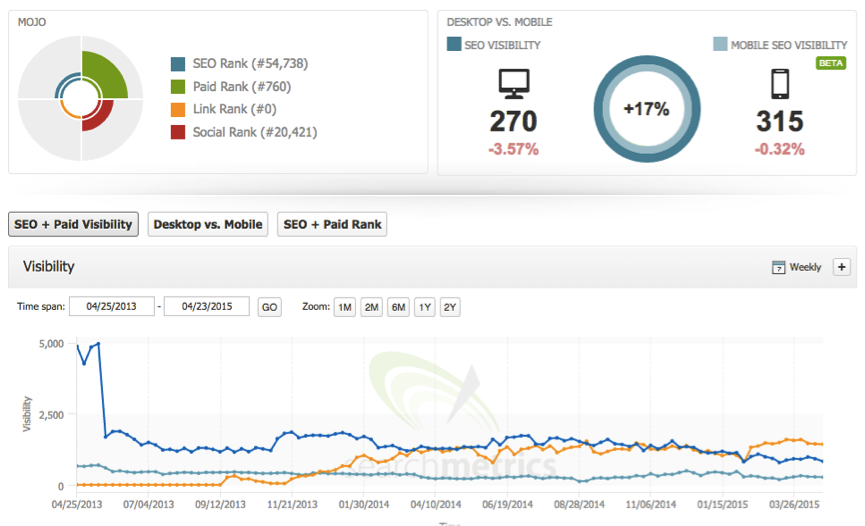
This shows the percentage difference between SEO/desktop and mobile visibility, which in this instance is 17 percent – this is not a bad difference. Below that is the graph that includes competitor visibility and this allows you to see how your website is performing overall against competitors.
7. Organic Keyword Rankings
Knowing the overall performance of a competitor is useful as this gives you a general feel for the level of the competition, but knowing what your competitor actually ranks for provides much more information.
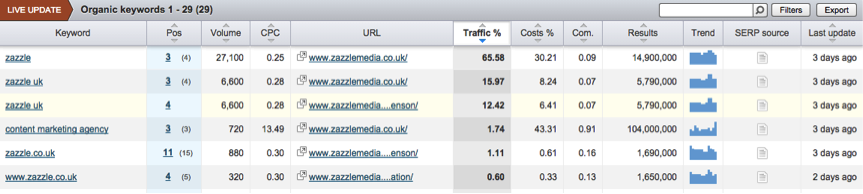
Using SEMrush, you’re able to export all organic rankings of a competitor. Enter the domain into SEMrush, go to “Organic Research” and click on “Organic Positions.”
The image below shows you this area of the dashboard and you can export the entire organic ranking report to allow you to have this raw data. This report looks at all rankings in the top 20 search results of organic search and the column “Traffic %” highlights the importance of each organic keyword to the competitor.
8. Organic Keyword Rankings in Common
To compare direct organic performance against a competitor, SEMrush has a tool that allows you to do this – it’s called “Domain vs. Domain” under their “Tools” section.
The image below shows you a visual representation of how many keywords each website ranks for and how many of those keywords are in common. You’re able to quickly work out that for all of what John Lewis rank for, 27.2 percent of those are directly in competition with House of Fraser.
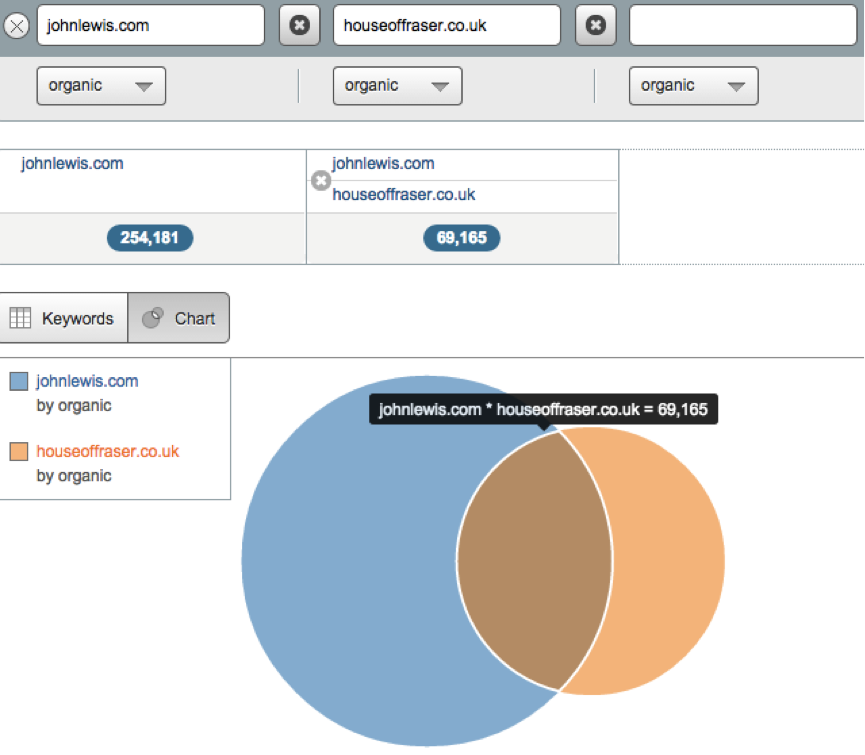
The keywords tab allows you to directly download all of those keywords that are in common and by simply adding the formula =IF(B1 < >””,IF(B1=MIN($B1:$D1),1,0),0) you’ll be presented with a visual representation of who ranks best for each individual keyword.
9. Organic Competitors
This area of SEMrush provides a list of sites that rank in the top 20 results of google.co.uk for the same search queries as you, or your competitors. The third column shows the amount of common keywords of these domains and your website or competitor.
Knowing your competition from a vanity perspective, or brick-and-mortar storefront (if applicable) is one thing, but direct online competition is sometimes unknown due to the smaller players that build significant organic presence.
This tool either confirms what you already knew, or allows you to look into new competitors.
10. Organic Traffic Generated From Keyword Rankings and Position Split
Within the Organic Research > Positions area of SEMrush, a table is presented above the rankings – this shows traffic generated by the keywords ranking within the top 20 positions in Google and the position split of those, 1-5, 6-10, and 11+.
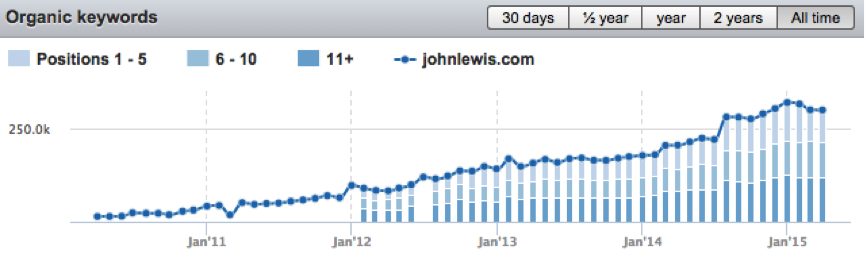
This comes into use when comparing your website’s position split against your competitors. If you rank for the same keywords, but you have a higher percentage of keywords residing in the 11+ split, the overall traffic projection is going to be lower due to the poorer click through rate.
11. AHREFs – Content Explorer
Once you have established who your competitors are, or established who you want to emulate in regards to growth and visibility, the ahrefs top content tool allows you to see the best-performing pages on the website in terms of referring domains and total social shares.
This tool has proven vital in part of our competitor analysis process as it highlights what is working for other websites. You can see an image of this tool in use below.
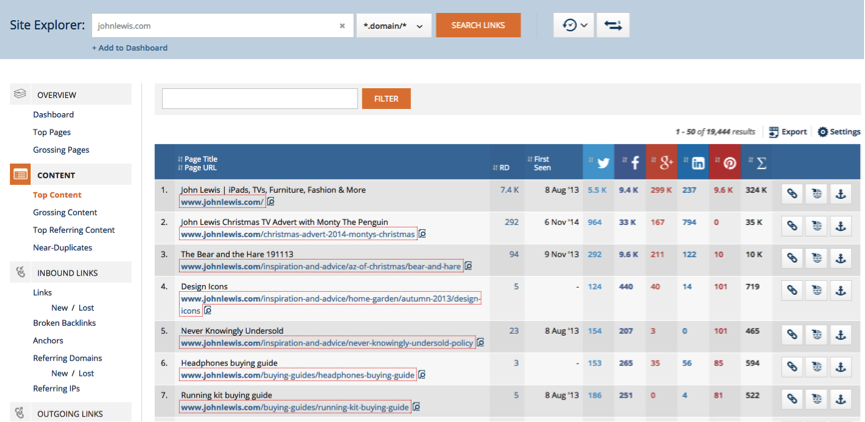
From this initial analysis, you’re able to see that for Johnlewis.com the top performing content pages are.
There is a common theme in this top performing content as the buying guides are performing very well in social and their TV Christmas campaign the “Bear and Hare” received a lot of links.
With this tool, it gives you a top line idea of well performing content that isn’t brand-specific (remove the TV campaign from the list above for yourself) to then dig deeper in regards to content ideas and keyword research.
12. AHREFs – Content Explorer
Once trends have been analyzed with regards to content types and topics that are working for your competitors, with ahrefs you’re able to see what content has performed best in terms of links and social shares with the Top Content tool.
A buying guide on running kit was highlighted above as a piece of content that has done well for John Lewis so through searching for “running” content with this tool, you’re able to specifically see which pieces of running related content have acquired large numbers of shares and links – see image below.

Through reverse engineering your competitors’ content strategy, you’re able to create a data-lead content strategy that will out perform your competitors due to this extra level of detail.
13. Social Shares
The content explorer and Buzzsumo tool are very similar regarding what content they return for topic related searches. But Buzzsumo focuses purely on social activity and has a broader reach. Below is an example of a “running” related search.
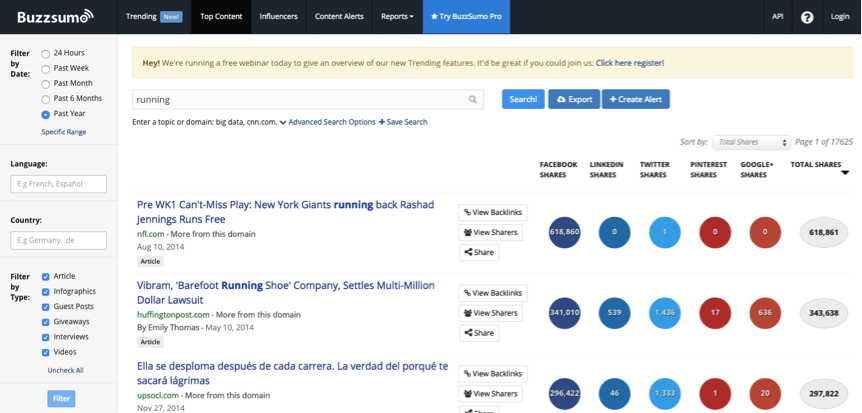
The best thing about Buzzsumo is that you’re able to create alerts for each topic you want to follow – this will be formed from the reverse-engineered content strategy of competitors.
14. URL-Level Metrics and Social Shares
URL Profiler gives you the capability to see the metrics of each individual URL of your competitors’ website, including Majestic’s trust and citation flow and social shares.
Below is an example export of this report (once cleaned up) and the most useful area of this report is seeing how the number of backlinks and referring domains directly impact the URL’s trust and citation flow.
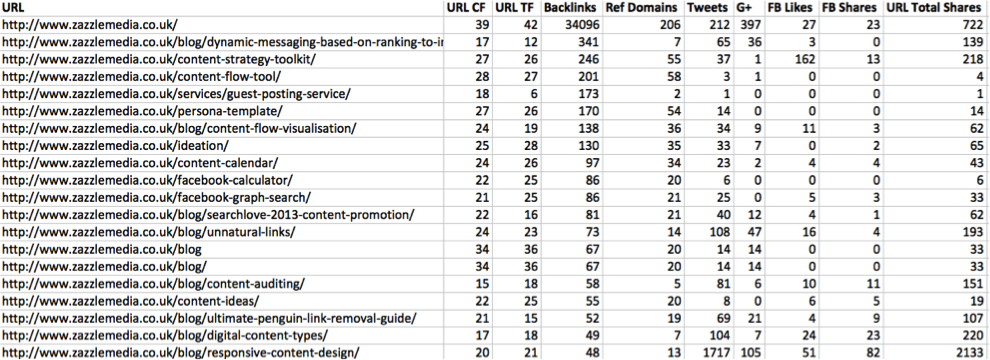
Once a URL has been identified as having good links, due to the increased trust and citation flow, this gives you the knowledge to export the links pointing into that URL to see where they’re getting them from as they’re inherently working.
Link-Building Strategy
So far we have established what your competitors’ site structure is, user experience metrics, top-performing URLs, and content – the last thing we should look at is link-building strategies for your competitors.
High-performing content through a mixture of research, as shown above in this analysis, does generate natural links and social shares, but there is still a lot of value in executing link-building strategies from external websites for your organic SEO campaigns.
15. Link Velocity
Measuring and investigating a competitors’ link-building activity can be identified through looking at the volatility of link velocity. Spikes in the velocity of new and lost links show either link-building activity or removal work, if a suspected penalty is in place for the competitor you’re investigating.
Through lots of these types of analysis, we have identified ahrefs as the freshest source of new links (within the last 30 days).
Below shows you a graph and how we visualize it as activity of potential removal and link-building activity. It’s important that you analyze this graph with a pinch of salt, as mass numbers of links can drop through a simple sitewide link being removed.

However, if you notice a competitor suddenly begin ranking well for a lot of keywords that they previously weren’t, this graph suddenly becomes very important in the analysis of that unforeseen growth. If the growth in organic search comes closely after a spike in link velocity, you are able to put two and two together.
16. Domain-Level Metrics and Topical Trust Flow
When analyzing the strength of your competitors, domain-level trust and citation flow are key in determining the strength and validity of your competitors.
The areas to focus on are the domain-level metrics, then the most relevant trust flow topic breakdown – see below.
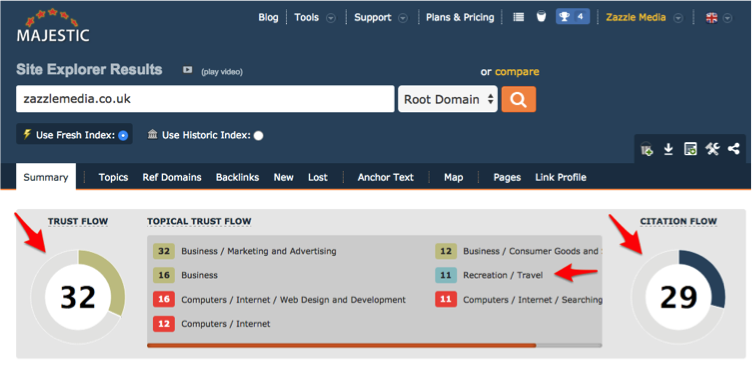
The rule of thumb for trust and citation flow metrics is that there should not be more than a 50 percent difference between the two – if so it’s a poor-level website.
Take a note of your competitor’s domain-level trust and citation flow. Compare against your own and you then have a general feeling of what the task ahead of you is. If the metrics are much more significant than yours, link equity needs to be built into the website to get closer to your competitor and if it’s less than your competitor, it may be link relevance or technical issues that are hindering your website.
For link relevance, topical trust flow is very helpful. As shown above with the topical trust flow breakdown, the relevance is very high for this website, bar recreation/travel. If all of the topics were irrelevant to what the website provides, the overall link quality may be low or they’re actively building links.
The topics that are highly relevant to your competitor and are featuring high numbers of trust flow – you’re able to export all of those specific links, which allows you to see where they’re acquiring these relevant links. Below is an image of what this looks like and you’re then able to replicate these links, if possible to acquire the high levels of relevancy that your competitor has.
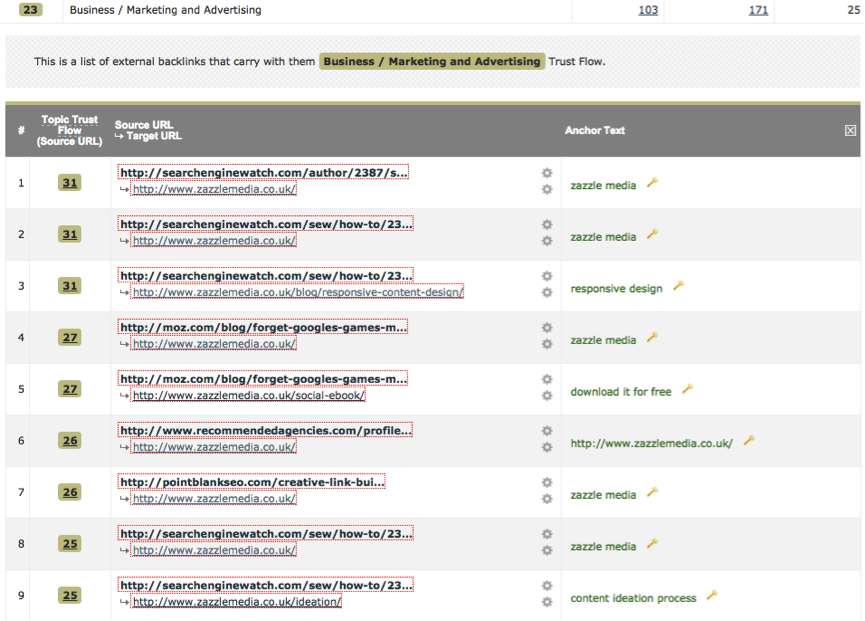
These links above are all relevant to the website and if you were able to replicate them, you would also establish this high authoritative relevancy and as a direct result, perform better in organic search.
SUMMARY
This step-by-step guide will allow you to gain a thorough understanding of your competitors’ organic strategies; using data to identify opportunity and helping you align your search approach accordingly to beat the competition!














