Each day your business remains local is a day of missed opportunities. In our global economy, it’s crucial your company extends the reach of its presence across national borders.
Consider this statistic:
There are roughly 300 million citizens in the U.S.; best-case-scenario, this equates to 300 million U.S. consumers. At first glance, the stats seem encouraging. Why should companies branch out of the American market?
Consider the Asian-Pacific, middle-class market. It stands at approximately 550 million today. That’s quite a staggering difference. Not only that, but that number is expected to grow to more than 3 billion by 2030, representing two-thirds of the world’s middle-class population. You do the math. An international strategy is crucial not only because it increases market shares, but also because it promotes brand expansion.
As more and more people acquire access to smartphones (estimated 1.75 billion in 2014), marketing to a local audience will seem practically provincial. Does this mean you should water down your brand identity? Not at all. On the contrary, this strategy is applicable to even the most exclusive brands.
Our comprehensive guide will show you how to utilize SEO to achieve your global-market goals. Truly, mastering these techniques will unlock your business’ multinational potential.
The New Face of Niche Marketing

If your company’s strategy is to corner a niche segment of consumers, you should be courting an audience that’s multicultural. You need to be both specific and inclusive. Consider it a numbers game; more potential clients equate to more potential business.
It’s time to position yourself as a player in the multilingual, global economy.
Creating Your International Online Marketing Strategy
The medium is the message. Or at the very least, it’s essential to pick the right site structure to convey the desired message. What do you use? Subdomains? Subcategories? Thoughtful analysis is essential before you can come to a conclusion.
1. Think Beyond the “Goobvious”
Thanks to the company’s massive global market share, we’ll be primarily discussing Google. However, since we’re focusing on international markets, it’s essential that we address other countries’ popular search engines. The Czech Republic favors Sezam, China is enamored with Baidu, and Japan prefers Yahoo. However, Google caters to its international clientele by employing country code top-level domains (otherwise known as ccTLDs). Keep this in mind when you’re drafting your international strategy. You want to maximize SEO exposure across country domains and alternate search engines.
2. Foundations: Research, Structure, and Goals
Before creating your marketing plan, we need to analyze crucial factors to determine what resources should be utilized for your project.
First, is your business actually ready to become international? Even with strict budgeting, expanding your Web presence to reach a global market will require substantial monetary and time investments.
A few things to consider:
- Can you set up a local office? If the answer is no, do you have the resources needed to set up a virtual office?
- Do you have bilingual customer service representatives? If no, do you have the resources necessary to hire professional translators?
- Will you employ separate marketing teams for each country? If not, is your current team equipped to advertise to a different culture?
- How is your tech support team? Are they able to manage multiple website hosts, or will you have to employ more staff?
You need to hash out your:
- tech support
- maintenance and security
- content development
- links and landing pages
- media outreach for each country
Use Google’s analytics to determine whether or not your business has an international audience to help you hone in the countries/languages with the greatest opportunity.

By clicking on Audience > Geo in Analytics, you can discover your site’s most popular countries and narrow your audience down into smaller regions like states and cities.

While collecting this data, determine the most commonly used languages. Use this information about international traffic in order to hone your business strategy.
If it turns out you don’t currently have an international base, you can employ market research to suss out international viability. Tools like Google’s Global Market, Finder, and Search Metricsare all particularly helpful. Make specific international goals and strategize accordingly.
3. Consider International Ranking Signals
As most of you know, Google uses more than 200 ranking markers in its algorithms, and many are given increased significance when analyzing international markets:
Top-Level Domains: These domains are country-code specific. They’re also top-level domains (with names like .co, .uk., and even .au.) These are trusted for their marked local affiliations.
Server location: Although this factor is becoming less important thanks to the growth of cloud hosting, it’s still a component to consider. Hosting in the country your company is targeting can give you a leg up.
Geo-Targeting: Site owners have the capability to alert Google to the country their site is targeting.
Local Signals: Inbound links from local websites help Google correctly place the target region.
4. Site Architecture
Determining whether you want to use ccTLDs, subdirectories or subdomains is a major consideration when going global. In this section we’ll explore the pros and cons of each:
A Brief Overview of ccTLDs:
For the uninitiated, ccTLDs is short for country-code top-level domain names. In other words, ccTLDs help search engines appropriately target geographical locations.

The Good:
- Geographic signals can help to improve local rankings
- Decreases the importance of server location
- Each site can be tailored to unique different local audience
The Bad:
- Without a local presence, they can be difficult to acquire
- They require substantial monetary commitment
- They rely on additional infrastructure
- You will need a different SEO strategy for each individual domain (and possibly more man power as a result)
A Brief Overview of Subdomains
Subdomains are versatile; they can be hosted individually but actually exist within the gTLD (generic top-level domain name) of an already registered domain. Subdomains can also be language or location specific.

The Good:
- Can be geo-targeted separately using Webmaster Tools
- You can host each subdomain on a separate host (local hosting)
- Easy to separate the sites and set up
The Bad:
- Each subdomain has to be treated as a unique domain which requires a separate SEO strategy
- No benefit from Google in terms of clear geo-targeting
- Local Searcher bias: Users may skip over your results because they prefer to visit local sites
A Brief Overview of Subdirectories
Many marketers prefer subdirectories because they have the capability for authority to be passed from different sections of a website.
The Good:
-
- Authority can be passed across the domain, making for a pleasant user experience
- Subdirectories are simple to set up and can be implemented after-the-fact within your existing site structure
- They can be geo-targeted individually by employing use of Webmaster Tools
,li>No need for separate domains equals much lower cost
The Bad:
-
- In terms of geo-targeting, subdirectories show the weakest signal
- It can be difficult to delegate which information needs to appear on the homepage
,li>Subdirectories are subject to local searcher bias. In other words, users might skip over your results in favor of a familiar, local site
5. The Language Vs. Geography Debate
First, are you attempting to target by country or language? Language targeting might be best if your product is information based. Therefore, your site needs to be language-centric. On the other hand, if you ship your product, geographical location is important to consider. Here national focus is more appropriate.
6. Hreflang Tags: A Must in Your Arsenal
It’s important to consider hreflang tags. Using these tags, you can create language page sets, and tell Google what language/country each page is targeted for. Below, you will see three different locations on your site where Hreflang tags can be used:

So you may have one page translated into five languages, if you tag them all together, Google will know it’s the same content but targeted at different people based on language or location.
Determining Objectives – The Hardest Part of Your Strategy
This is where things tend to get complicated. No two businesses are identical. Therefore, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach.
For businesses with enough budget and resources, it’s ideal to create country-targeted websites with country ccTLDs. This is ideal as you will send Google the most powerful geographical ranking signals. However, you’ll need to build country-specific links and have the capability to manage multiple domains.
The next best approach is to use subdirectories. The benefit is that you can use Webmaster Tools to set the geo targeting for each folder. In addition, if you build authority for the DOMAIN, this will help improve visibility for each of the subdirectories hosted on the same domain.
Subdomains are considered separately from subdirectories, and have to build unique Domain Authority. They can be integrated with the same design and geolocated with Webmaster Tools.
Every business will have different objectives and resources, so your first step will be a comprehensive analysis of goals and resources so you can determine the best approach.
Moving Forward…How to Start?
So now that we’ve explored domain architecture, how do you integrate some of these important elements?
First, be considerate of your global audience; be conscious of client needs. Avoid codes that force customers into an unfamiliar language or country-specific IP addresses. Internationalization is only effective when you provide options for your users to find the language, specific currency, and even global location that fits their consumer requirements.
These elements/tips will really separate your business from the pack:
- Translate your URL’s and ensure you utilize country-specific keyword research.
- Make separate language options prominent and easy to use.
- Use both localized titles and descriptions for each page. This might require extra research, but is worth the extra time!
- Give customers easy access to customer service and create localized contact and support information. Companies like TollFreeForwarding will help you create a local phone number for each country.
- Don’t forget to take advantage of Google’s Local Business Center.
- Edit currency to fit each country’s consumer needs.
- Translate everything, even parts of your menu.
- Make sure you even remember to translate alt tags!
- Make sure comments are translated, too, so clients feel confident about posting a product review or engaging in dialogue.
As you can see, the key to international success is attention to detail and diligence. If you prioritize creating a great international user experience, you will reap the benefits. Make sure Google can accurately understand your target audience, and you will be well on your way to global expansion.
International Marketing for Your Business
It’s time to break down a few key strategies for your international marketing debut…

Content Marketing:
- Create a blog with engaging content in all the target languages! Be sure to regularly update with keyword-centric content
- Be conscious of linking and use “link bait” to attract pageviews
- Utilize cultural elements as part of your content focus
- Use infographics and other eye-catching images
Outreach for Link Earning:
- Use your content assets to connect with other bloggers in the target language and country. Create a network of bloggers who can leverage each other’s Web presence
- Collaborate with your new connections on high-end content
- Earn local links on the subdomain/subdirectory level. Use local business directories to help in your efforts. Ensure consistency with name, address, and other local citations.
- Don’t forget to focus on earning links in your targeted language! Don’t be afraid of other language sites. For example, link to sites that are only in French. If you need to run a site through a translator, do it. Having links to sites written in different languages will improve your website’s relevance.
Analyzing Your Competitors:
- Use tools such as moz.com and ahrefs. Look at sites that are flourishing, with a good ranking.
- Next, analyze these companies’ link profiles. You can use them as a base for earning similar links. (Note: make sure the links are good and won’t lead to unwanted penalties.)
Promote Your Content. It’s Time to Start Using Social Media and Paid Amplification!
- Use social media to pick out your target audience’s favorite topics and/or buzzwords. Tools like Buzzsumo and Topsy are wonderful for this.
- Share your content on your company’s social media pages.
- Don’t be afraid to invest in paid social media ads.
- Make good enough content, and you can reach out to industry influencers to convince them to promote your contributions.
Remember that at its core, international marketing isn’t so different from the type of marketing you’ve been launching for your current, local website. Your new strategy simply requires a few easy modifications that allow you to localize your site for your target country or language.
You’ll be happy to know that generally, Google’s ccTLDs are less competitive than Google.com’s analytics. Start with ccTLDs, gain a dedicated client base, and work your way up. It’s really that simple!
Ways to Track Your International Marketing Efforts
It’s time to talk about tracking your international marketing efforts via the amazing tool that is Google Analytics. Google analytics will allow you to track ccTLDs, subdomains, and even subcategories. You do this by filtering your subdirectories.
Simply go to Admin > All Filters and click on “New Filter.”

Enter the name of the filter and select “include only” “Traffic to the subdirectories” “that are equal to.” The next step is just to add the relevant directory you wish to track:
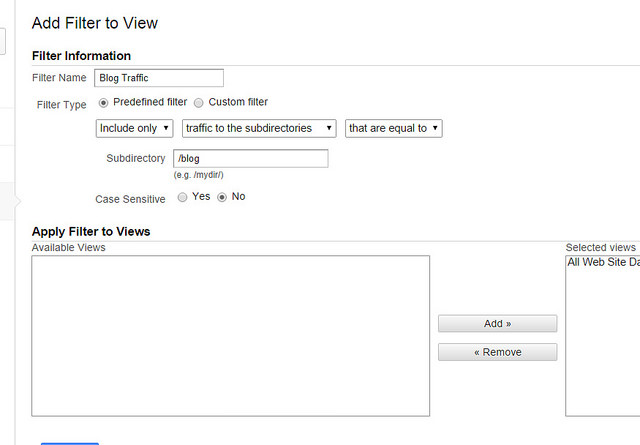
For a thorough guide for mastering this process, click here. Once you’ve learned how to read the analytics, you’ll be able to implement different marketing strategies, eliminate any that aren’t working, and improve your marketing’s effectiveness.
Well, There You Have It…
The essentials to making your company multilingual and multinational. Are you ready to take your company international? We sure hope so. Now go on and plan your worldwide, online takeover! You’ve got this!








